How Much Protein I Need By Age And Gender
Discover exactly how much protein I need by age and gender. Learn the optimal daily intake for health, muscle growth, and weight management.
How Much Protein I Need By Age And Gender
Why Protein Is Essential for Your Health
Protein is more than just a gym buzzword — it’s a vital nutrient your body needs every single day. Made up of amino acids, protein is the building block of muscles, skin, enzymes, hormones, and even your immune system. Whether you’re aiming to build strength, manage your weight, or age well, getting enough protein can make a noticeable difference in how you feel and perform.
What Protein Does in the Body
- Builds and repairs muscle tissue
- Supports immune function
- Produces enzymes and hormones
- Maintains healthy skin, hair, and nails
Key Benefits of Eating Enough Protein
- Muscle maintenance & growth: Crucial for athletes and older adults to prevent muscle loss.
- Better metabolism: Protein has a higher thermic effect than carbs or fat, meaning you burn more calories digesting it.
- Longer satiety: Helps control cravings and overeating.
- Faster recovery: Speeds healing after exercise, injury, or surgery.
How to Calculate Your Daily Protein Needs
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) Explained
The current RDA for sedentary adults is 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This is the minimum needed to avoid deficiency — not necessarily the optimal amount for performance or health. Here is an easy formula to find out how much protein I need by age and gender.
Simple Formula for Finding Your Protein Intake
Convert your weight to kilograms (divide pounds by 2.2).
Multiply by:
0.8 for a sedentary lifestyle
1.0–1.2 for light activity
1.2–1.6 for moderate activity
1.6–2.0 for heavy training or muscle building
Example: 70 kg (154 lbs) active person → 70 × 1.6 = 112 g protein/day
Why Your Protein Needs May Be Higher Than the RDA
- Age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia)
- Intense training
- Weight loss while preserving muscle
- Recovery from illness or injury
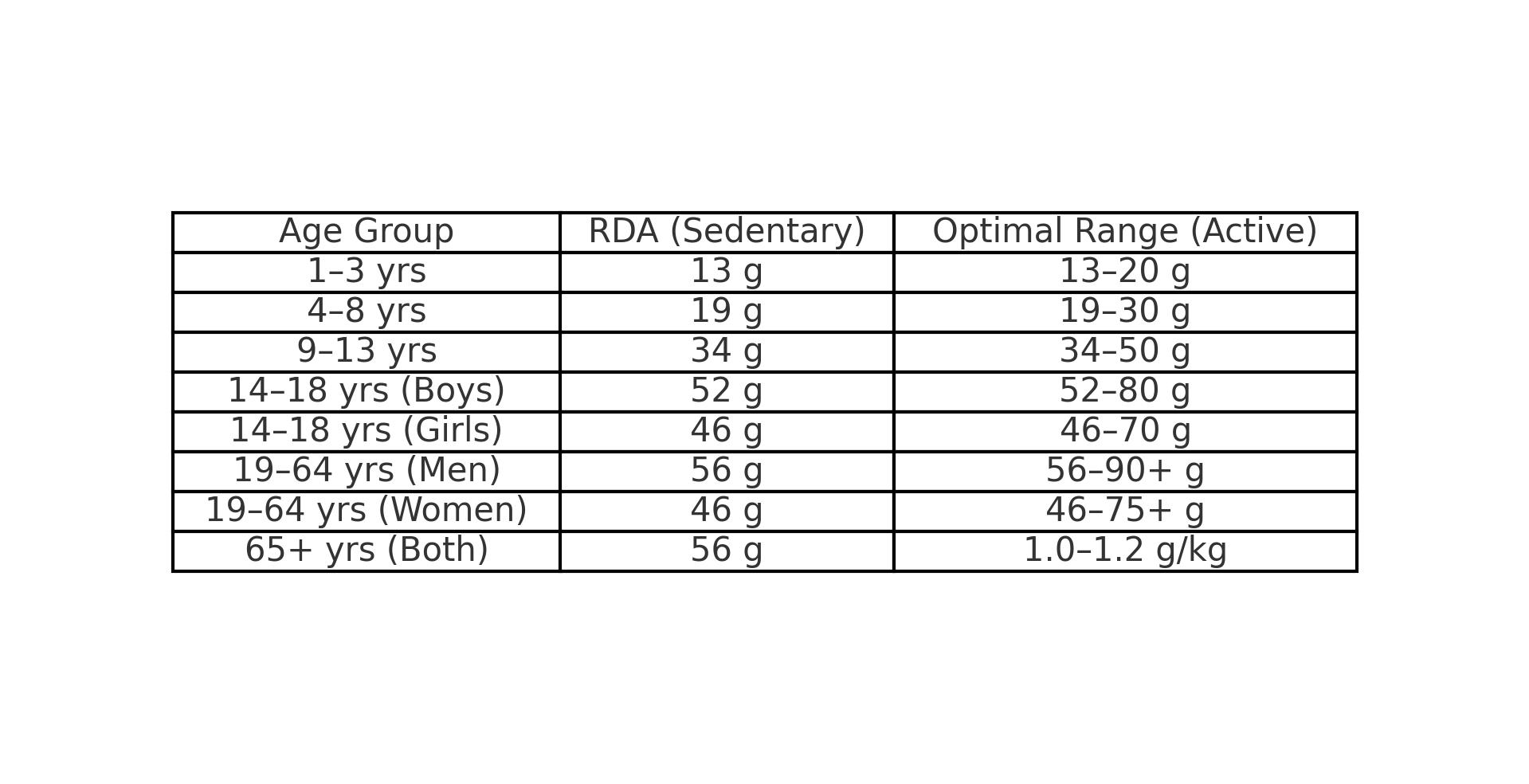
Protein Requirements: How much protein I need by age and gender
| Age Group | Gender | RDA (Sedentary) | Optimal Range (Active) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–3 yrs | Both | 13 g | 13–20 g |
| 4–8 yrs | Both | 19 g | 19–30 g |
| 9–13 yrs | Both | 34 g | 34–50 g |
| 14–18 yrs | Boys | 52 g | 52–80 g |
| 14–18 yrs | Girls | 46 g | 46–70 g |
| 19–64 yrs | Men | 56 g | 56–90+ g |
| 19–64 yrs | Women | 46 g | 46–75+ g |
| 65+ yrs | Both | 56 g | 1.0–1.2 g/kg |
Adjusting Protein Intake for Activity Level
Sedentary Lifestyle
0.8 g/kg body weight
Focus on balanced meals with lean proteins
Light to Moderate Activity
1.0–1.4 g/kg
Ideal for people who walk regularly, do yoga, or light gym workouts
Strength Training & Endurance Athletes
1.6–2.0 g/kg
Helps build muscle, improve recovery, and enhance performance
Recovery from Injury or Illness
1.2–2.0 g/kg
Supports tissue repair and healing
Best Protein Sources for Every Diet
Animal-Based Proteins
- Chicken breast (~26 g per 3 oz)
- Salmon (~22 g per 3 oz)
- Eggs (~6 g per large egg)
- Greek yogurt (~15 g per 6 oz)
- Lean beef (~25 g per 3 oz)
Plant-Based Proteins
- Lentils (~18 g per cup cooked)
- Tofu (~9 g per 3 oz)
- Quinoa (~8 g per cup cooked)
- Chickpeas (~15 g per cup cooked)
- Almonds (~6 g per 1 oz)
Protein Supplements
- Whey protein powder (~20–25 g per scoop)
- Pea protein (~15–20 g per scoop)
- Collagen peptides (~10 g per scoop)
Common Myths About Protein Intake
Is Too Much Protein Bad for Your Kidneys? In healthy people, high-protein diets are safe. Those with pre-existing kidney disease should follow medical guidance.
Can You Eat High Protein on a Plant-Based Diet? Absolutely — with proper planning, plant-based eaters can easily meet protein goals using legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, and protein powders.
Final Tips for Meeting Your Protein Goals
- Spread intake evenly: Aim for 20–30 g per meal
- Pair with fiber-rich foods: Keeps you fuller longer
- Mix sources: Combine animal and plant proteins for variety
- Stay consistent: Daily habits matter more than occasional high-protein meals
Bottom line: Your protein needs depend on your age, gender, and activity level. Use the chart titled: How Much Protein I need by age and gender, and formulas above to find your ideal range, and choose nutrient-rich protein sources to support your long-term health.
More About High-Protein Diet
The Ultimate Guide to a High-Protein Diet: 4 Benefits, Best Foods & Meal Ideas
How Protein Helps You Lose Weight and Keep It Off: 5 Reasons
Want More Energy? These 8 High-Protein Foods Are a Must